Ever wonder where the phrase “long in the tooth” originated? According to lore, nineteenth-century horse traders were the used car salesmen of their day, often misrepresenting their steed’s age to attract higher bids. To combat these questionable sales tactics, a wise buyer would check inside the animal’s mouth. If the teeth looked long, it meant its gums had already receded, suggesting the horse was likely older than claimed (i.e., “long in the tooth”).
Gum recession and the painful symptoms associated with it were once thought to be an inevitable sign of aging, but professional treatments and preventative steps can address the issue. Gum tissue does not grow back, so while gum recession is irreversible, there are things you can do to keep the problem from getting worse.
What are receding gums?
Receding gums occur when your gums pull back from the teeth exposing more of the tooth, including the roots. When this happens, gaps form between the gums and the teeth. Bacteria can gather in these gaps, causing periodontal disease and wearing away at the teeth. In advanced cases, the infection can start breaking down the bone underneath, causing tooth loss.
Gum recession is a very gradual process, and many people don’t realize they have receding gums until it’s already occurring. Signs of gum recession vary, but can include red or swollen gums, bad breath, mouth sores, and pain or bleeding when brushing or flossing.
Professional Treatments
Depending on the cause and severity of your gum recession, your dentist may recommend one of the following procedures:
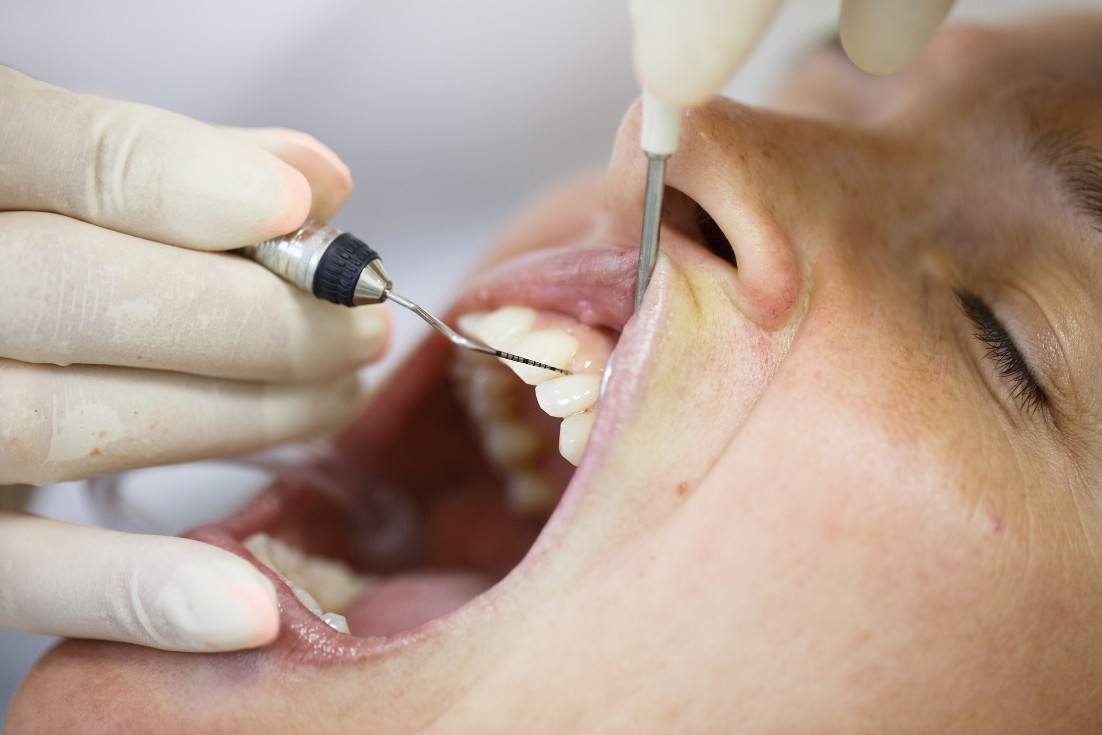
Deep Cleaning – A deep cleaning, also known as root planing or tooth scaling, can help address mild gum recession. During this process, the gums are peeled back to expose the roots of the teeth, which are then smoothed down. Because bacteria have a more difficult time attaching to smoother surfaces, this process helps to protect your teeth and gums from infections. Sometimes an antibiotic gel is applied to the teeth during the cleaning to kill hard-to-reach germs; other times, oral antibiotics or a special antibiotic mouth rinse might be prescribed.
Surgery – If your gums already have pockets that are too deep or you’ve experienced too much bone loss, a deep cleaning won’t be enough to treat the gum recession. In these instances, surgery may be necessary. Bone regeneration and tissue or gum grafts are two procedures frequently recommended to address receding gums.
- Bone Regeneration – Regenerative surgery is needed when you’ve lost bone and gum tissue. The process is similar to a deep clean and root planing, but in addition to folding back the gums and cleaning the affected area, a material that encourages your body to regenerate tissue and bone on its own will be applied before the gums are secured over the roots again.
- Tissue Graft – If too much gum material has been lost, a gum tissue graft may be needed to restore the gums. If enough material is available, this tissue can come from elsewhere in your gums. Alternatively, it can be taken from the roof of your mouth.
Gum Recession Prevention
Regardless of the cause of gum recession, preventative measures should still be taken to keep it from advancing. The following tips reduce your risk of receding gums and increase your overall oral health:
Quit Smoking – Tobacco usage can increase the harmful bacteria in your mouth. Quitting will prevent tooth decay, gum recession, and other harmful side effects of smoking.
Maintain Proper Oral Care – Taking proper care of your teeth is essential to overall oral health. Brushing twice a day, flossing regularly, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can improve teeth and gum health and prevent additional gum recession.
Choose Healthy Foods – Not only do crisp fruits and vegetables help reduce plaque, but the vitamins and nutrients from healthy food can also help discourage the growth bacteria in your mouth. Since bacteria thrive on sugars, avoiding sugary foods is a good way to prevent gum irritation.
Visit the Dentist – Regular dental visits (i.e., every six months at a minimum) is the best way to stay on top of your oral health. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that can cause gum disease and allow your dentist to monitor gum health for any signs of gum disease.
Treat Existing Conditions – Crooked teeth, a misaligned bite, or teeth grinding can increase your risk for gum disease and receding gums. Treating these conditions reduces the wear and tear on your gums and teeth and your risk of gum recession.
Contact Our Office
If you notice any signs of gum recession it’s essential to contact us immediately so we can begin the process of treating and preventing further damage to your gums. If you’re experiencing symptoms, or have questions or concerns, please reach out to our dental team.

